In the intricate world of Electronic Design Automation (EDA), engineers often face a steep learning curve when mastering complex tools. Remembering every API, its precise syntax, and the nuances of various options can be a significant hurdle, even for experienced users returning after a break. This frequently leads to repetitive consultations of user manuals, diverting valuable time from core design tasks.
The advent of cost-effective Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened a new paradigm: enabling users to interact with EDA tools using plain, natural language. This revolutionary approach allows engineers to simply describe their desired modifications, and the tool intelligently translates these instructions into executable commands.
GOF ECO leverages this capability to introduce AI-Powered Natural Language ECO operations. As illustrated in Figure 1, users can now choose between the traditional, strict API syntax or a more intuitive natural language approach to perform complex netlist modifications, such as inserting a specific inverter type to alter a pin's logic.
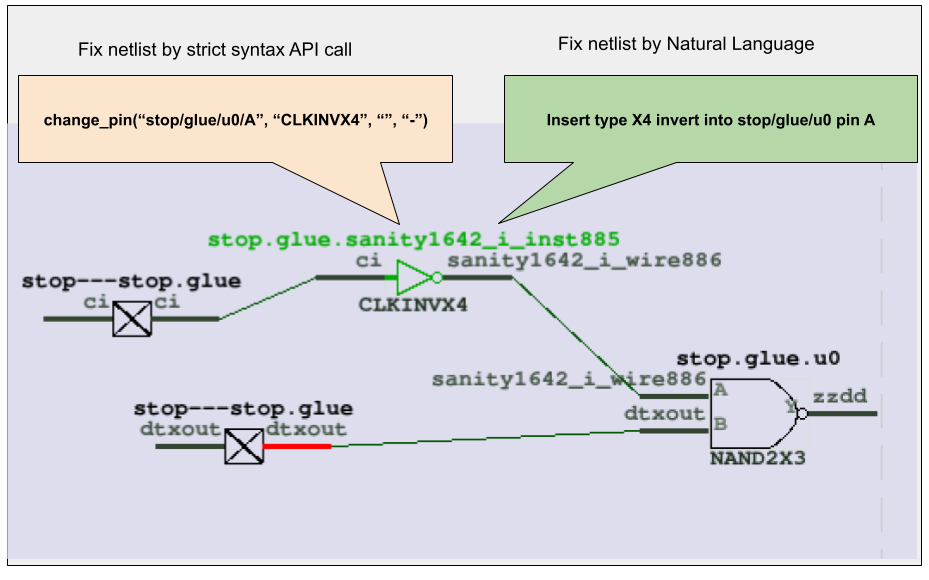
Figure 1: Using Natural Language to Modify Netlist Logic
Traditionally, implementing a change like inserting an X4 inverter into a specific pin requires adherence to a precise API syntax. This often involves a detailed review of the user manual to locate the correct command and consulting the library file to identify the exact component name (e.g., 'CLKINVX4').
The Conventional API Call Method:
change_pin("stop/glue/u0/A", "CLKINVX4", "", "-")
With the LLM-driven approach, users can bypass manual searches and directly articulate their intent:
Insert type X4 invert into stop/glue/u0 pin A
At its core, the AI-powered Natural Language ECO in GOF operates through a sophisticated translation layer. When a user inputs a natural language command, the LLM processes it to:
Example script for Natural Language ECO operations:
# AI powered Natural Language ECO operations use strict; # To catch script syntax issue # Setup ECO name 'auto_svf' setup_eco("auto_svf_example"); read_library("/lib/5nm/tsmc_typ_85c_078v_svt.lib"); # Read in standard library read_design("-imp", "/proj/ai_acc/post/implementation.gv"); # Read in Implementation Netlist file Which is under ECO set_top("topmod"); set_ai(1); # Enable AI run_nl("Insert type X4 invert into stop/glue/u0 pin A"); # NL ECO run_nl("Change pin B of stop/glue/u0 to fun_clk"); run_nl("Insert a NAND into stop/glue/regsame/D pin, insert a MUX into B pin of the NAND, connect the MUX S0 pin to net bi, connect the Mux B pin to a new inserted AND gate, the AND gate is driven by net dft_clk and pin mmux0/du0/Y, connect the MUX A pin to net ci"); write_verilog("eco.gv");